City Gates
BACKGROUND
Locations
In ancient and medieval times, cities were generally surrounded by large walls for defense. Access was limited to the points where major roads from the surrounding towns passed through the walls.
Function
Gates allowed the city inhabitants to block access to the city at night and when threatened by hostile forces.
CHARACTERISTICS OF ROMAN GATES
Appearance of Impregnability
Ancient city gates were intended to not only be impregnable but also look impregnable.
Arcuated Construction
As with other types of Roman construction, the round arch was used.
Ornamental Use of the Orders
Using the orders to decorate city gates added an element of refinement to the masonry masses. The decorative element was important because gates expressed the prestige of the state.
Rustication
The rough surfaces and prominent joints of the rusticated masonry contributed to the fortified appearance of Roman gates.
INFLUENCE ON LATER ARCHITECTURE
Influence of Weaponry
Later, with the invention of gunpowder and the development of the cannon at the beginning of the Renaissance, city walls became more emblematic than practical.
Renaissance
The adoption of Roman models for Renaissance gates was especially appropriate in the case of fortified architecture because of Rome's past military might. The ancient Roman use of heavily rusticated masonry and ornamentation by the orders were used in the Renaissance by architects such as Sanmicheli and Michelangelo.
EXAMPLES OF ANCIENT CITY GATES
Etruscan Gates
♦Porta Augusta, Perugia
Roman Gates
♦ Porta Appia (Porta San Sebastiano), Rome
♦ Porta Maggiore, Rome, AD 52
♦ South Gate, Jerash, Jordan, 129-30
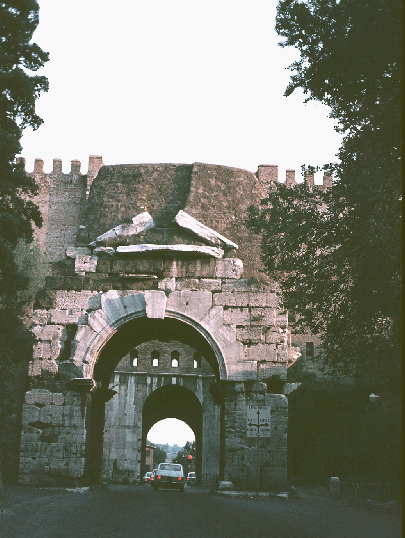

Porta Appia (Porta San Sebastiano today), Rome



 Add Placemark
Add Placemark Go Back
Go Back